We’re excited to share our latest publication “Spin-Valley Polarization Control in WSe2 Monolayers using Photochemical Doping”, in Advanced Optical Materials. This outstanding work was carried out by researchers from the Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser (IESL/FORTH) - Eirini Katsipoulaki, Georgios Kopidakis, Emmanuel Stratakis, George Kioseoglou and Ioannis Paradisanos - in collaboration with Konstantinos Mourzidis, Vishwas Jindal, Delphine Lagarde, Xavier Marie from INSA-CNRS (France), Takashi Taniguchi and Kenji Watanabe from the National Institute for Materials Science (Japan), and Mikhail M. Glazov from the Ioffe Institute (Russia).
Summary
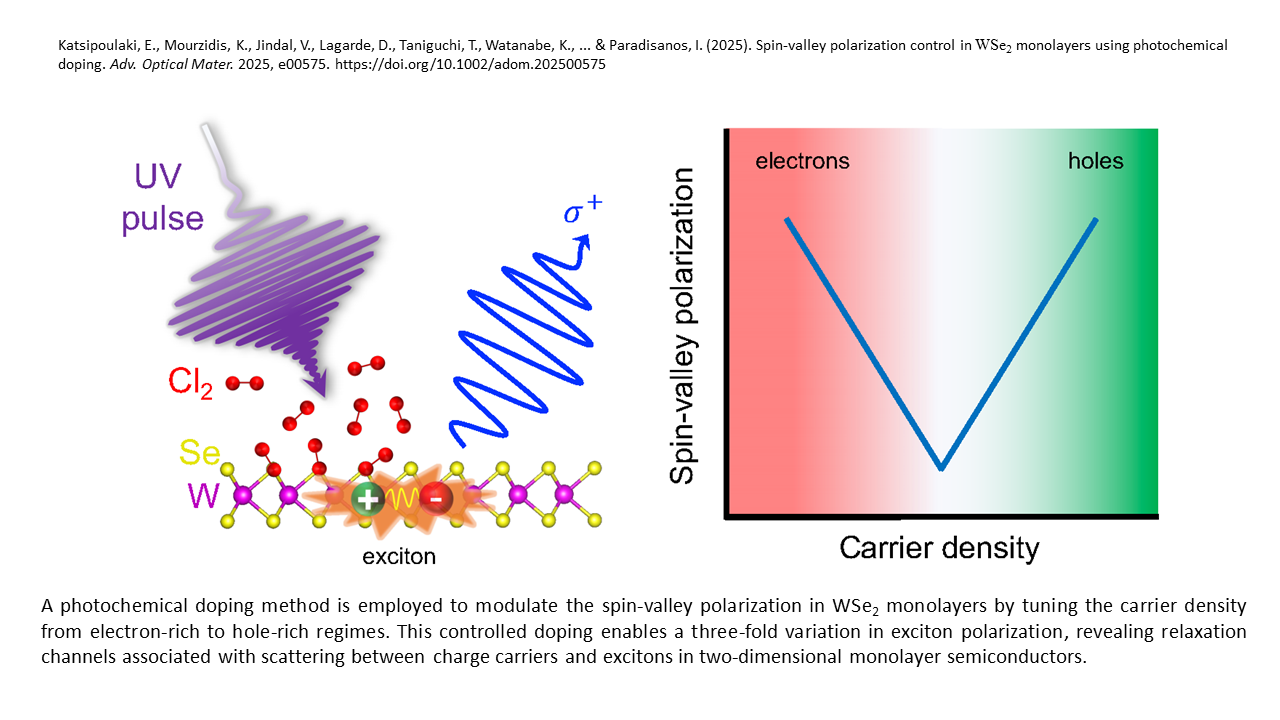
This recent study advances our understanding of the exciton spin relaxation in the limit of strong scattering with carriers and control of the spin-valley polarization degree in transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) monolayers, a key step toward developing valleytronic and optoelectronic applications.
First time observations:
1. New tuning mechanism of spin-valley polarization: a precise, single-shot photochemical doping method eliminates the complexities of electrostatically-gated devices, offering a practical approach for studying valleytronic properties in TMDs.
2. Optical emission readout of the impact of both electrons and holes in the spin-valley relaxation process.
3. Strong tunability of exciton’s circular polarization degree: a threefold modulation was achieved in the carrier density range studied.
Reference
E. Katsipoulaki, K. Mourzidis, V. Jindal, D. Lagarde, T. Taniguchi, K. … & I. (2025). Paradisanos, Spin-Valley Polarization Control in WSe2 Monolayers using Photochemical Doping. Adv. Optical Mater. 2025, e00575. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202500575


