- PERSONAL INFORMATION
Family Name, First Name : Tzallas Paraskevas
Researcher unique identifier: Paraskevas Tzallas on Google Scholar [2]
Date of birth : Grevena-Greece, Feb. 4, 1974.
Nationality: Hellenic
Office address : Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas, Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser (FORTH-IESL), N. Plastira 100, Vassilika Vouton, 70013, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, Tel.: +30-81-391127, Fax: +30-81-391305, e-mail: ptzallas@iesl.forth.gr
- CURRENT POSITION (S)
2017-now: Research Director (Researcher A') at the Foundation for Research and Technology – Hellas (FORTH), Greece, and head of the "Quantum light and Technologies" and "Attosecond science and technology" activities at FORTH.
2024-now: Coordinator of the Center of Quantum Science and Technologies of FORTH (FORTH-QuTech)
2014-now: Senior Research fellow and Scientific Advisor at Extreme Light Infrastructure-Attosecond Light Pulse Source (ELI-ALPS), Szeged, Hungary
- PREVIOUS POSITIONS
2002-2004: Post-Doc in MAX-PlANCK-INSTITUT FÜR QUANTENOPTIK in Garching (Germany)
2004-2017: Researcher D', Researcher C' and Principal Researcher (Researcher B') at FORTH-IESL
2018-2020: Board member of the scientific council of FORTH-IESL
- SHORT BIOGRAPHY: I received his PhD in physics in 2002. Then, I joint as PostDoc fellow the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics (MPQ) in Garching, Germany. Then he moved as researcher at FORTH, rising on 2017 to the rank of the Research Director.
- CAREER BREAKS (2004): 6 Months military obligation in the Greek Armed Forces. I was acknowledged by the Greek Ministry of National Defence as a Distinguished Scientist of Abroad.
- RESEARCH INTERESTS: Atomic, Molecular and Optical physics (AMO); Attosecond science and strong laser field physics; Quantum Optics and quantum information science.
-
EDITORIAL DUTIES:
2020: Guest Editor in the special issue on "Quantum optics in strong laser fields" of the journal Photonics.
2024: Editor of the book on the 'High-order Harmonic generation in solids', which is published by World Scientific, which is the exclusive publisher for the Nobel Foundation, and they have over 100 titles by Nobel Laureates and on the Nobel Prize.
2025-now: Editorial board member of the J. Phys. B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical physics.
- RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
My scientific contribution in the research fields of Quantum Optics and Technologies, and Attosecond Science, is characterized by the development of many novel approaches and research highlights. Below I summarize some of them.
Quantum Optics and Technologies:
- Non-linear optics using intense optical Schrödinger CAT states Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 013601 (2025).
- Connection between Strong-laser-field physics, non-classical light states and quantum information science (Rep. Prog. Phys. 86, 094401 (2023), Phys. Rev. A 109, 033706 (2024), J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 58, 132001 (2025)).
- Generation of high photon number optical Schrödinger CAT states with controllable quantum features (Phys. Rev. A 105, 033714 (2022) (Editors' suggestion))
- Generation of high photon number non-classical and entangled light states from extreme-ultraviolet to far infrared spectral range (Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 123603 (2022), PRX Quantum 4, 010201 (2023), Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 143603 (2024)).
- Generation of optical Schrödinger CAT using intense laser-matter interactions ( Nature. Phys., 17, 1104 (2021)).
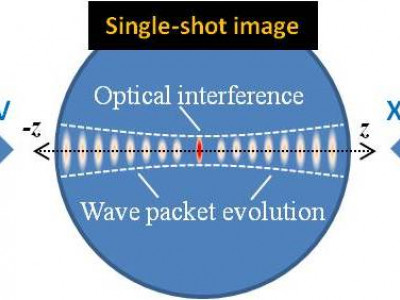
- Development of a method namely "Quantum Spectrometer" which has been used for the generation of optical Schrödinger "cat" states using intense laser-matter interactions (Nature Commun. 8, 15170 (2017); Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 193602 (2019)).
Attosecond Science:
- Attosecond pulse metrology: The first direct observation of attosecond light bursts emitted from gas and solid-state media [Nature 426, 267 (2003); Nature Phys. 5, 124 (2009); APL Photonics 4, 080901 (2019). Comparative studies between 2nd order autocorrelation and cross-correlation methods (RABBITT) [Phys. Rev. A 82, 021402(R) (2010)].
- Generation of intense isolated Attosecond pulses. Development of a method that leads to the generation of high-power coherent continuum XUV radiation (Nature Phys. 3, 846 (2007)). Development of the highest energy ever reported Attosecond source (Phys. Rev. A 98, 023426 (2018)).
- XUV non-linear optics: The first observation of atomic direct double ionization by a harmonic superposition (Phys. Rev. A 74, 051402(R) (2006)). The first observation of multi-XUV-photon multiple ionization of atoms using tens of Gigawatt power XUV pulses (Phys. Rev. A 98, 023426 (2018)). Implementation of an ion imaging detector for quantitative studies in the linear and non-linear XUV regime (Phys. Rev. A 90, 013822 (2014); Sci. Rep. 6, 21556 (2016)). Implementation of an ion imaging detector in ultrafast molecular dynamics using electron quantum path interferences (Phys. Rev. A 100, 061404 (2019))
- XUV-pump-XUV-probe studies. Tracking of the sub-fs dynamics in atoms and molecules (Nature Phys. 7, 781 (2011); Phys. Rev. A 89, 023420 (2014) (Editors Suggestion)).
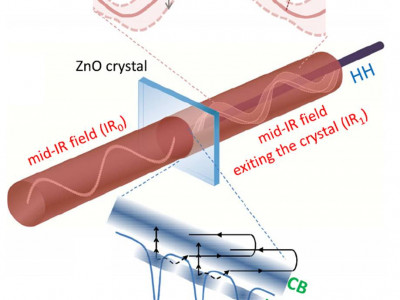
- Attosecond science using VUV attosecond pulses emitted by strongly laser driven semiconductor solids. Attosecond spectroscopy using vacuum-ultraviolet pulses emitted from laser-driven semiconductors (Nature Commun. 16, 1428 (2025).
- PUBLICATIONS IN INTERNATIONAL REFEREED JOURNALS: 100 published papers, including 1 Nature, 5 Nature Phys., 1 Nature Photon., 1 Rep. Prog. Phys., 2 Nature Comm., 1 PRX Quantum, 9 Phys. Rev. Lett., 1 Physics Reports, 15 Phys. Rev. A, 3 Optica, 1 Opt. Lett., 6 Sci. Rep., 7 New J. Phys., 8 J. Phys. B, 2 Optics Express, 2 Appl. Phys. B, 2 Chem. Phys. Lett., 2 J. Phys. Chem. A etc., 8 chapters in books, and 8 Invited review/perspective articles in international scientific journals.
- Invited/Keynote talks in Conferences/Colloquia/Workshops: > 68 including 3 Keynote.
- REFEREE IN INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC JOURNALS: Reviewer in international scientific journals including, Nature, Nature Photon., Nature Phys., Rep. Prog. Phys., Nature Commun., Phys. Rev. Lett., PRX, PRX Quantum, Phys. Rev. A, J. Phys. B, Optica, New J. Phys., Optics Letters, Physical Chemistry, etc.
- PROPOSAL REVIEWER: 1) Austrian Science Fund funds (FWF); 2) German Research Foundation (DFG); 3) Israeli Higher Education Committee/ Israeli Atomic Energy Commission (IAEC); 4) French National Research Agency’s (ANR); 5) Hellenic Foundation for Research & Innovation (HFRI); 6) European Research Council, ERC Advanced Grant.